Network Cabling Montreal-Laval-Quebec
What do you mean by Network Cabling ?
- Typically, information is transferred between network devices using cable as the medium. Many different kinds of cable are frequently used with LANs. A network may use only one type of cable in some circumstances, while in other scenarios, a network may use a range of cable types.
- The size, topology, and protocol of a network all influence the kind of cable that is used for it. For a network to be developed successfully, it is essential to comprehend the properties of various types of cable and how they connect to other parts of a network.
What is a Cable Drop ?
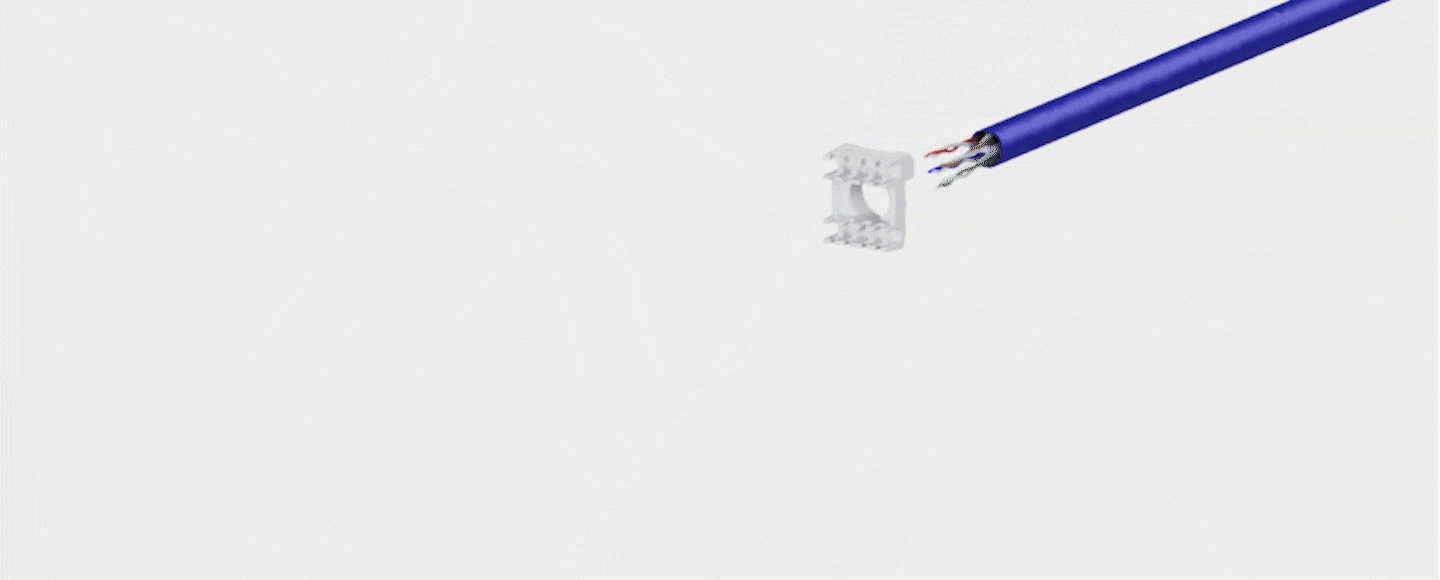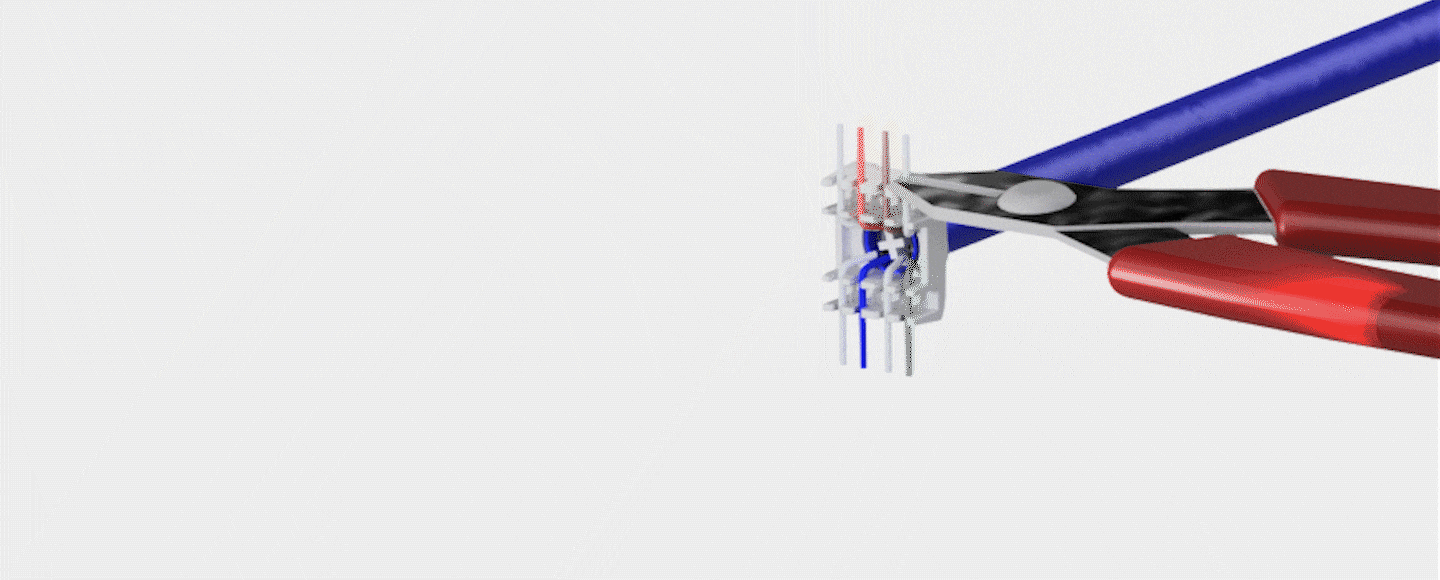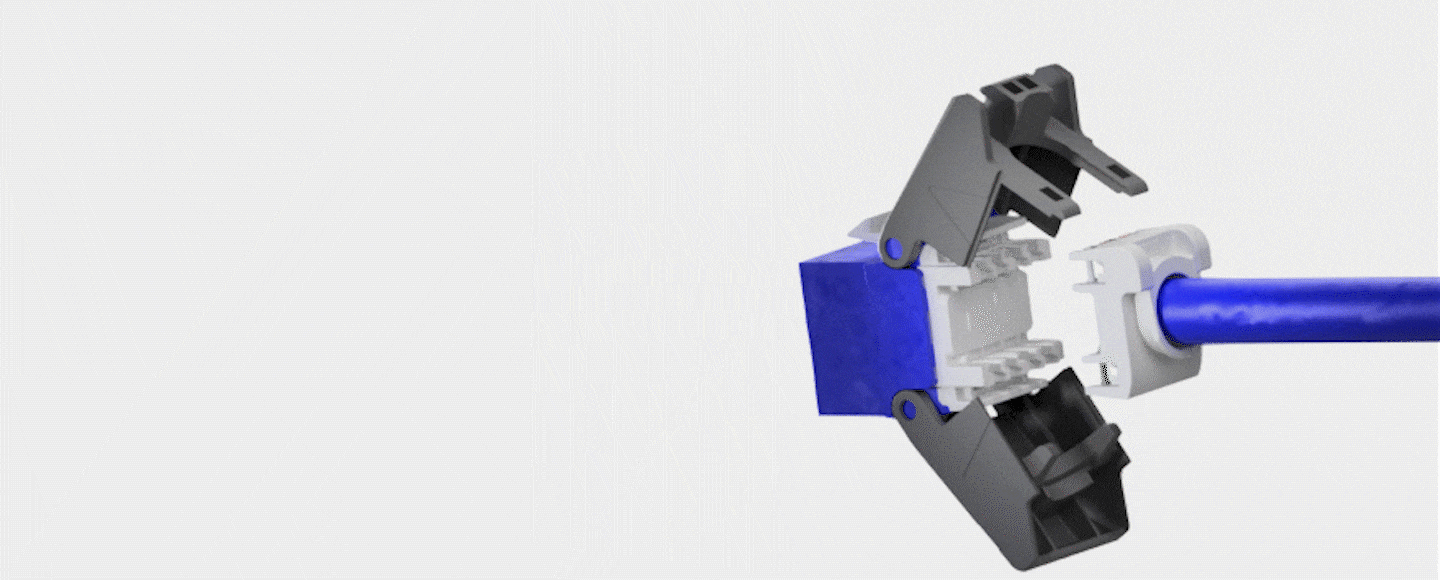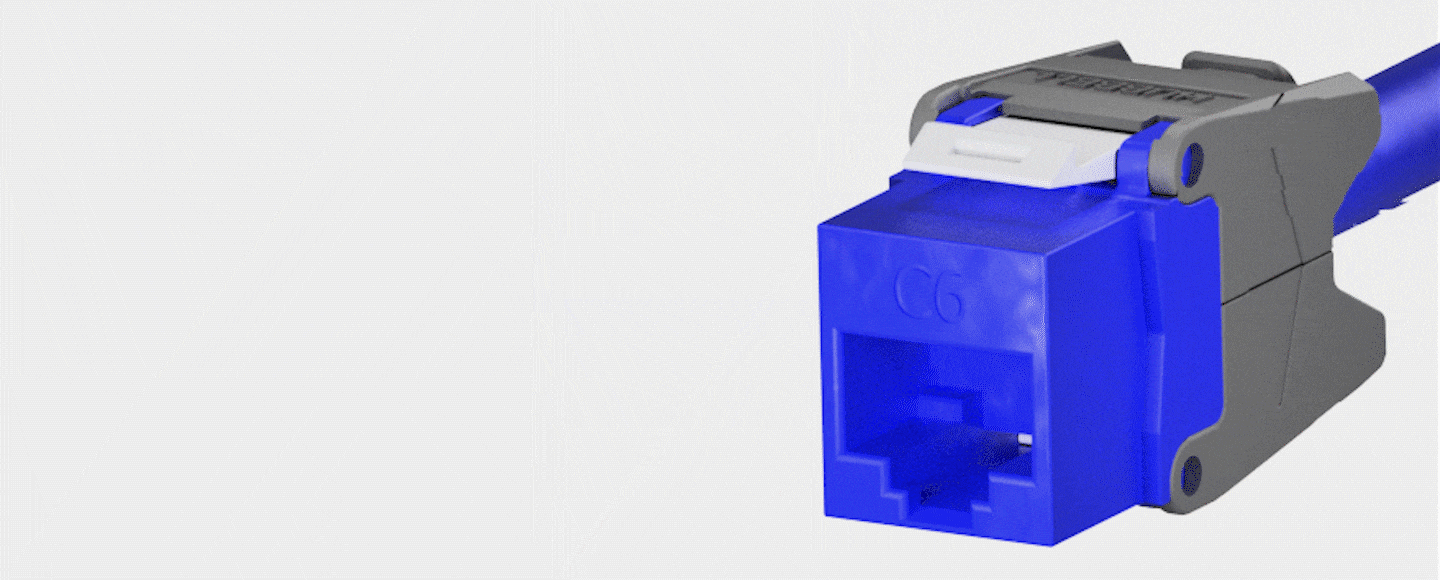
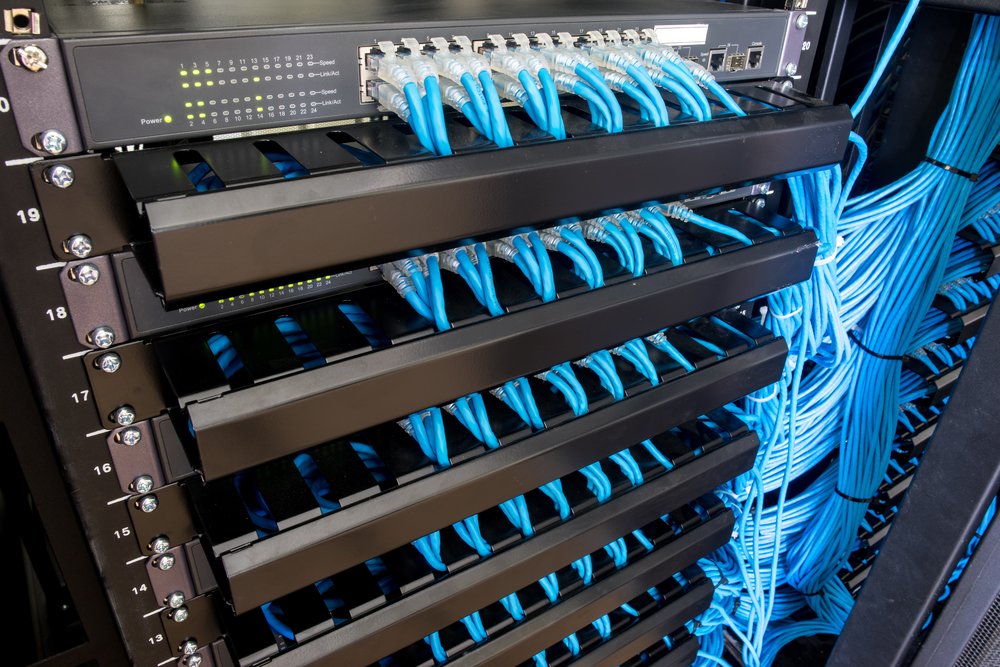
- A network cabling drop refers to the physical connection point where network cabling is terminated at a specific location, such as an office or a data center. It is the point where the cabling infrastructure is connected to network devices such as computers, switches, routers, servers, or other networking equipment.
- In practical terms, a network cabling drop typically consists of a length of network cable, terminated at both ends with connectors that match the devices being connected, and installed through the walls, ceilings, or floors of a building to reach the desired location. Network cabling drops can be made using different types of cables, such as twisted-pair copper cables (e.g., Cat 5e, Cat 6,Cat 6e,Cat7), fiber optic cables, or coaxial cables.
- The type of cable used depends on the specific requirements of the network being deployed, such as the distance to be covered, the bandwidth needed, or the environment in which it will be installed. Overall, network cabling drops are essential components of any structured cabling system and are used to create a reliable, high-performance, and secure network infrastructure.
What are types of cabling in network?
- A network device can be connected to one or more other network devices using networking cables, or two or more devices can be connected to a single computer or network device.
- Data and information are transferred between network devices using network cables as a conduit. The size, configuration, and topology of the network all affect the kind of cable that is used. The infrastructure of the network is supported by the many types of network cables.

1. Fiber Optic Cable
- A glass core in the middle of fiber optic cables is encased in several layers of protective material. They are ideal for settings with significant electrical interference because they transmit light rather than electronic signals, which avoids electrical interference.
- Due to their resilience to moisture and illumination, fibre optic cables have established themselves as the industry standard for tying together networks across buildings.
2. Coaxial Cable
- A plastic layer serves as insulation between the center conductor and braided metal cover of coaxial cables, which have a single copper conductor at their core. Fluorescent lights, motors, and other external computers cannot interact with the system because of the metal shield.
- Despite being difficult to install, coaxial cabling is highly resistant to signal interference. Compared to twisted pair cables, it can support longer cable lengths between network devices. Coaxial cables come in two varieties: thick coaxial and thin coaxial.
3. Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
- STP cables use a unique kind of copper telephone cabling that is specifically suited for business installations and are frequently referred to informally as just ethernet cables. The typical twisted pair of telephone wires are supplemented with an outside shield that serves as a ground.
- If you wish to install cables in a location where there may be electrical current interference and hazards from unshielded twisted pair cables, shielded twisted pair cables may be the ideal choice. Twisted pair cables with shielding can further increase the separation between the cables.
4. Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
- As ethernet cables and phone wires, unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables are widely used in the computer and telecommunications industries. To eliminate electromagnetic interference (EMI) from outside sources, wires of a single circuit are twisted around one another in a UTP connection.
What is an Ethernet cable?
- An Ethernet cable is a common form of network cable used in wired networks. (a network type which connects devices to the Internet or other networks using cables).
- They link devices on local area networks (LANs) such as routers, PCs, and switches.
- One of the most common wired networks employs cables linked via Ethernet ports on network routers, computers, and other devices.
What are the different categories of Ethernet cable?
- Cat1 : For a while, voice telephone systems in homes and workplaces were wired using this unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable. It was intended for analogue voice communications and was made up of two insulated copper wires that were wound around one another.
- Cat2 : In the 1980s, IBM Token Ring networks mainly employed category 2 cabling, which could handle voice and data connections. A 4 Mbps data transmission rate was supported.
- Cat3: When Category 3 cable was first introduced in the early 1990s, it contained four twisted pairs and was the first to enable both 10BaseT Ethernet networks and digital voice communications. Although it is still present in older structures, the 10 Mbps data rate is regarded as being too sluggish for contemporary networking.
- Cat4: Similar to Cat3, Category 4 cable is sometimes found in older buildings because full replacement would be too expensive. It was mainly used for IBM Token Ring networks and had a 16 Mbps data throughput.
- Cat5: Category 5 cable, which was first introduced in 1995, has a data throughput of up to 100 Mbps. It is employed in conventional 10BaseT and 100BaseT (Fast Ethernet) networks and has a range of up to 100 meters for the distribution of data, video, and telephone signals (328 ft.). Manufacturers refer to an upgraded Cat5 cable with rates of up to 1 Gbps as Cat5e, a term that is not officially recognized. By increasing the number of twists, it may transmit data at a greater rate while also being more crosstalk-resistant’s twists, it may transmit data at a greater rate while also being more crosstalk-resistant.
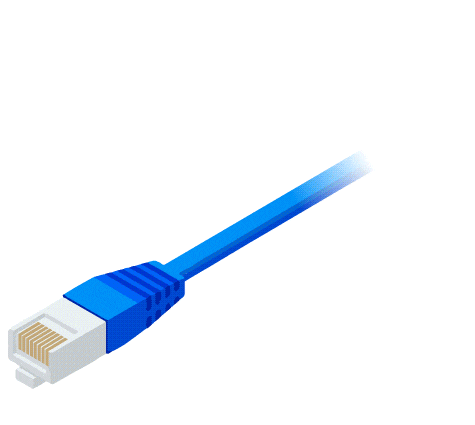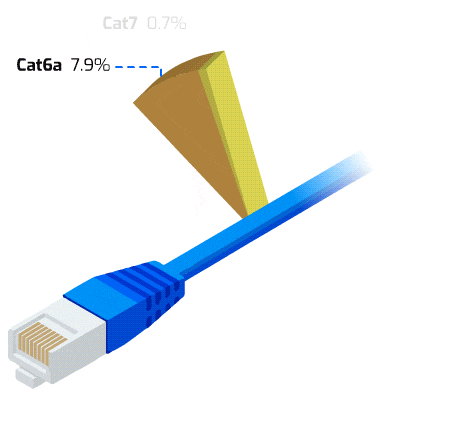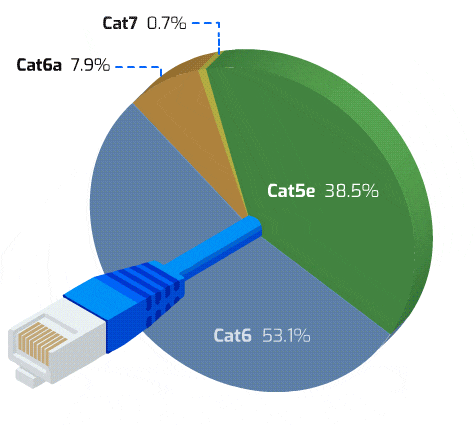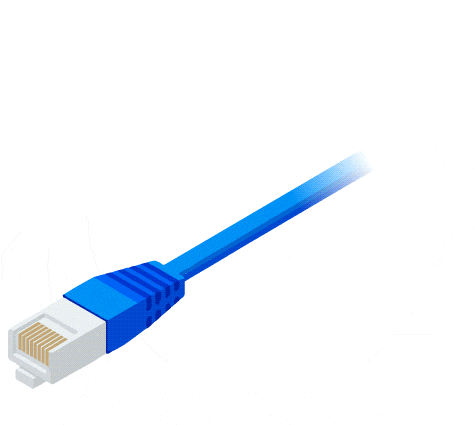
- Cat6: Cat6 cable offers more bandwidth and data transfer speeds up to 1 Gbps over 100 m, the same as Cat5e, in compared to Cat5e. However, due to its enhanced shielding and increased capacity, Cat6 is able to reach 10 Gbps speeds over shorter lengths of up to 37 m (121 ft). Cat6 contains foil shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference and a physical barrier between the four pairs known as a “spline” to reduce crosstalk. The Cat5/5e standard and Cat6 cabling are backwards compatible. Cat6a is a “augmented” Category 6 cable that was first introduced in 2009 and has a capacity of up to 500MHz.
- Cat7: The IEEE or TIA/EIA have not given their support to the Cat7 specification, which is a private standard created by a group of businesses. Although essentially equivalent to the performance qualities of Cat6a, Cat7 cables have robust shielding and exclusive GG45 connectors. A development of Cat7, Cat7a (Category 7 Augmented) offers 40 Gigabit speeds across 50 metres and 100 Gbps up to 15 metres. The Cat7 and Cat7a installed base is rather minimal due to the proprietary nature of the standards and the absence of IEEE and EIA support.
- Cat8: Cat8 cable is the best choice for switch-to-switch communications in a 25GBase T or 40GBase T network since it has a bandwidth of up to 2 GHz (2000 MHz) over 30 metres and a data throughput of up to 40Gbs. To essentially eliminate crosstalk and permit greater data rates, its wires are covered in foil. As a result, the cable has a larger gauge, is more stiff, and can be challenging to install in small locations. It is backwards compatible with earlier standards and continues to use RJ45 connectors.

What is an RJ45 cable ?
- An RJ45 cable is a type of network cable commonly used for wired Ethernet networks. It is also known as an Ethernet cable, network cable, or LAN (Local Area Network) cable. The term “RJ45” refers to the type of connector used on the cable, which has 8 pins and looks similar to a telephone jack.
- RJ45 cables are used to connect devices such as computers, routers, switches, and other network equipment to each other and to the internet. They are designed to transmit data at high speeds over short to medium distances, typically up to 100 meters.
- The cables come in various lengths and categories, with different specifications for speed and bandwidth. The most common type of RJ45 cable is Category 5e (Cat 5e), which supports speeds up to 1 Gbps. Other types include Cat 6, Cat 6a, and Cat 7, which support higher speeds and higher bandwidth.
- Overall, RJ45 cables are an essential component of many wired network setups, providing reliable and fast network connectivity for a wide range of devices and applications.
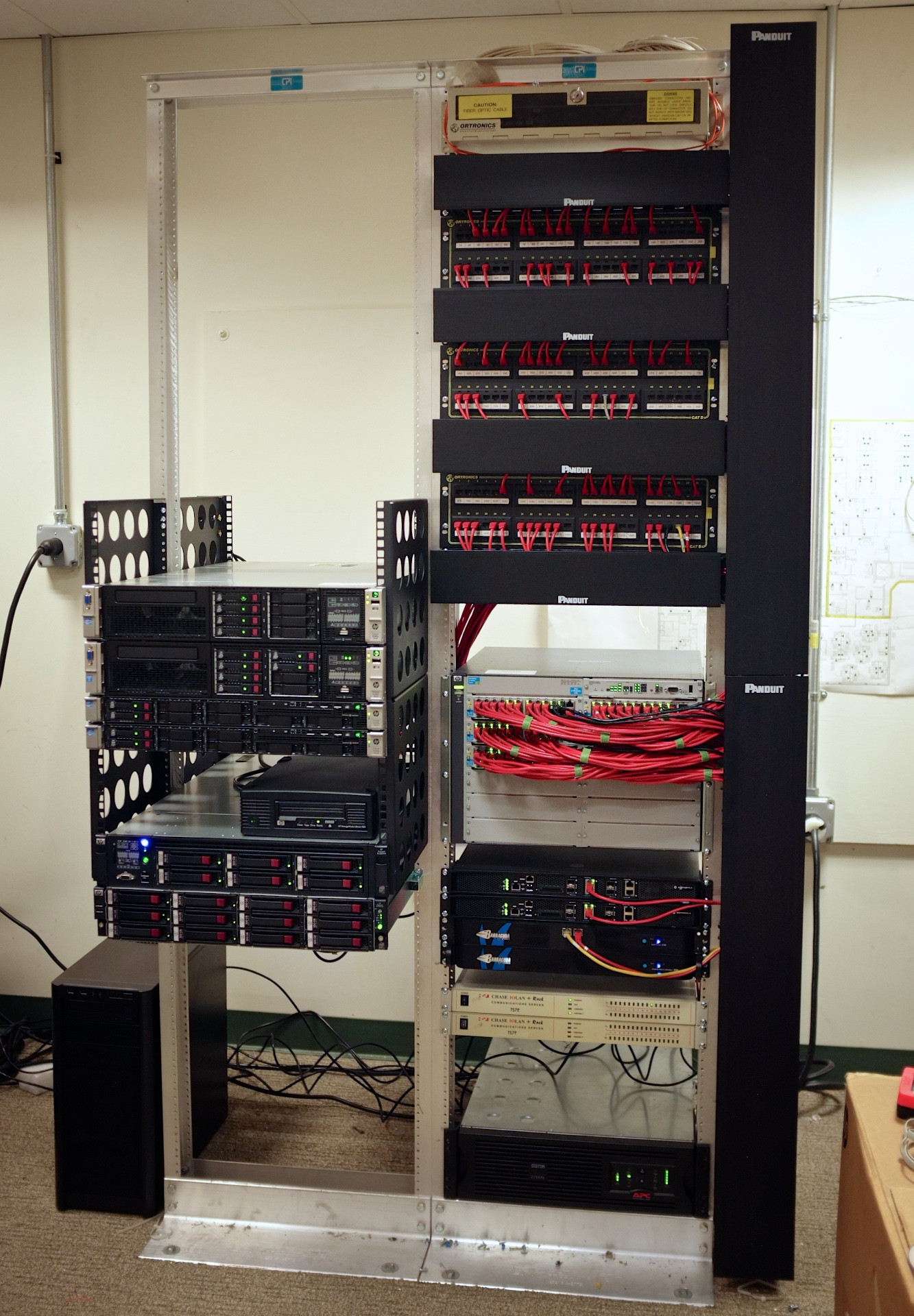
What Are Network Cabling Services?
- Functional IT networks are built on a foundation of cabling. To link and transfer data and other information between computers, routers, and storage systems, network cables are required.
- Network cables resemble a person’s veins. They act as transporters, allowing data to move between locations. Your company’s infrastructure is made up of network cables.
- IT specialists provide network cabling services. This include laying out the cabling’s framework as well as running and installing cables.
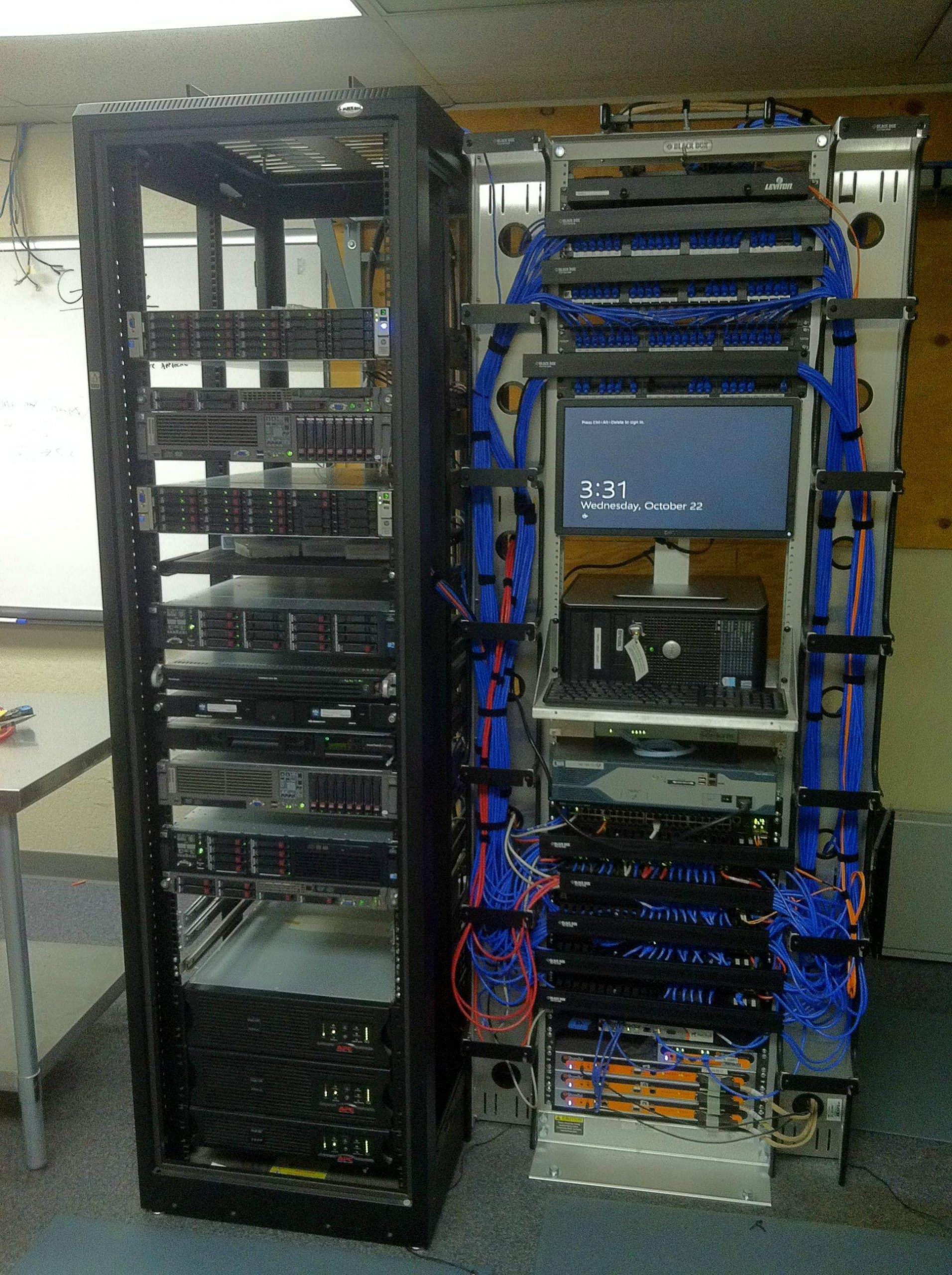
What is Structured Cabling?
When installed correctly, a structured cabling system can significantly improve the efficiency of your daily operations. Due to twisted cables, disorganized wiring can seriously affect connectivity.
A business’s structured cabling system cannot be built in a single way. Based on your requirements, your network cabling specialists will create and install a specific cabling solution. Your voice, data, and network cabling can be organized and secured more efficiently as a result.
 What are the Advantages of Network Cabling?
What are the Advantages of Network Cabling?
1. Easier to Isolate Problems
Whatever your line of work, you will eventually experience system failures. Your IT professional will be able to analyze and identify the issue more quickly if your network is organized.
As a result, there will be little downtime and income loss for your company. Your bottom line is impacted by good network cabling services from the beginning since they ensure that you can quickly resume operations after a breakdown.
2. Adaptability
- Technology is evolving at an amazing rate. However, it also implies that you must be ready to adapt new apps. The bandwidth of a structured cabling system is substantial. This implies that your network will be able to quickly embrace new apps when you need to do so.
- If you choose to install your cabling system correctly from the beginning, it won’t become obsolete.
3. Improved Safety
- In any job, health and safety are vital issues to discuss. A well-organized cabling infrastructure improves workplace security. The risk of fires, falls, and electric shocks are greatly increased by unkempt wires.
- By choosing to organize your network cables, you can concentrate on managing your business rather than worrying about the dangers in the server room.
4. Scalability and Simplicity
- Even as your business expands, maintaining the connectivity of your communication systems will be simple with proper network cable installation.
- Without altering the network’s design or changing the system’s structure, you may quickly add new features as they become necessary.
- A structured cabling system is a simple, well-organized system that you can choose to have. Your company probably depends on a variety of IT tools.

“Are you interested in installing your own data cabling in Montreal Laval Quebec area?”


“Give us a call TODAY for one of the most reliable and professional cabling team in Canada!”