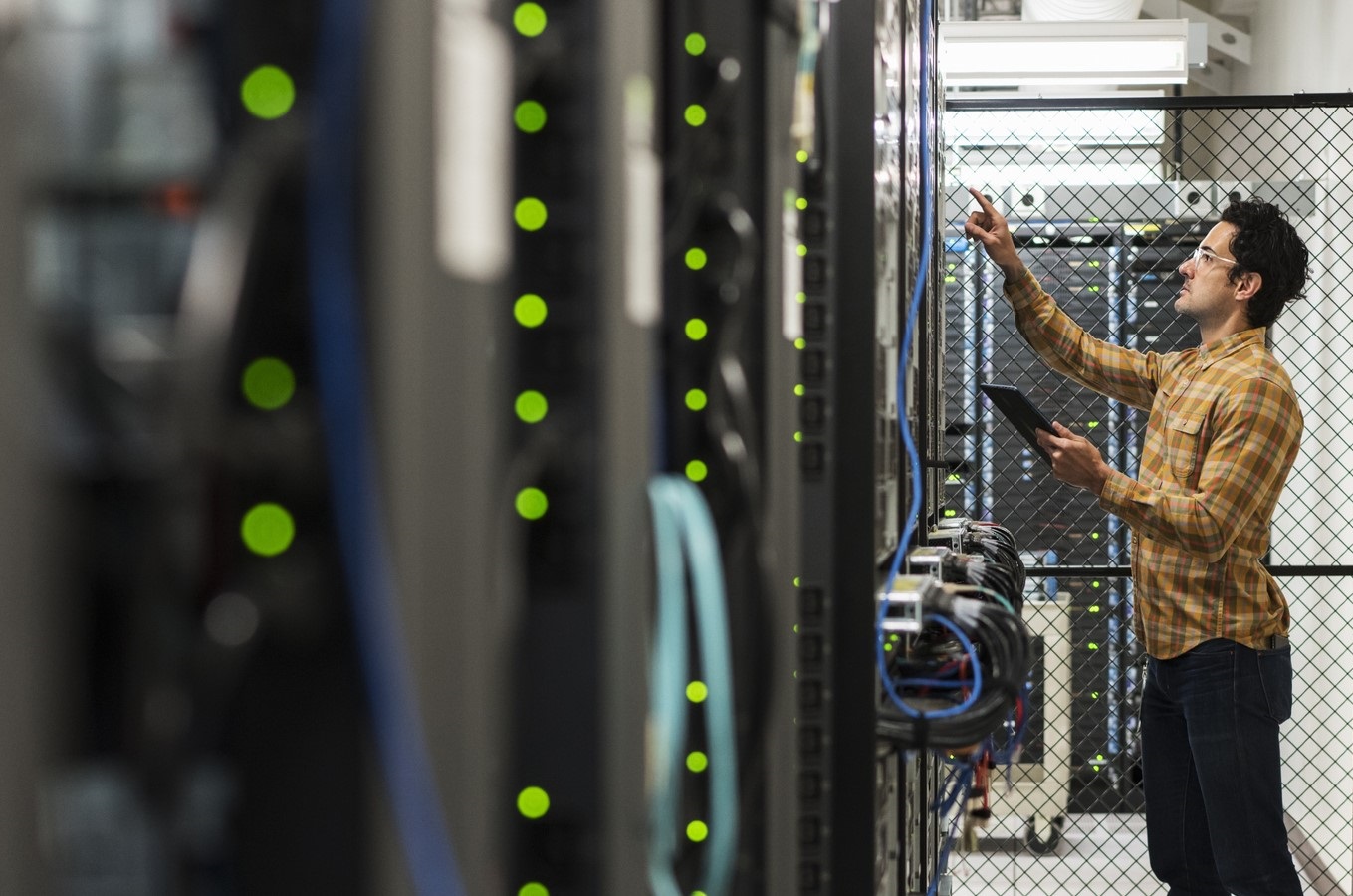
MANAGED IT SERVICES MONTREAL-LAVAL-QUEBEC
 CLOUD COMPUTING : ADVANTAGES VS DISADVANTAGES
CLOUD COMPUTING : ADVANTAGES VS DISADVANTAGES
- Cloud computing is when you outsource your entire business. For example, you can outsource aspects of storage or computational statistics so that you can direct your resources elsewhere.
- Cloud technology has advanced considerably in recent years. As a result, developed countries such as Canada have certain ways to address the challenges, challenges and opportunities posed by cloud technology. Let’s take a closer look at its the advantages and disadvantages.
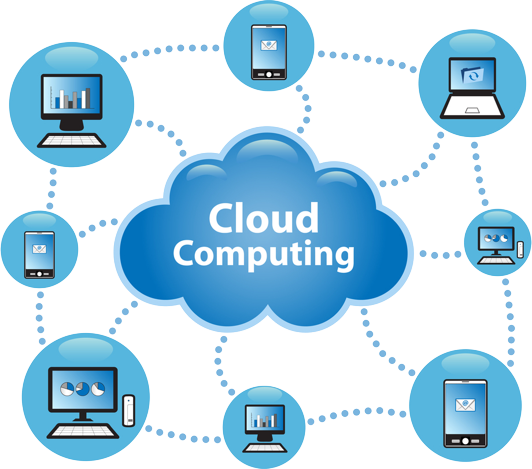
What are the main benefits of migrating to the cloud?
Here are some of the benefits that force organizations to migrate resources to the public cloud:
Scalability : Cloud computing can be scaled to support more workloads and more users, which is easier than existing local infrastructure. In traditional IT environments, companies need to purchase and configure physical servers, software licenses, storage, and networking equipment to maximize business services.
Costs : Cloud providers take over maintenance and upgrades, and companies that migrate to the cloud may incur low IT operating costs. They can provide additional means of innovation – developing new products or improving existing products. Migrating performance to the cloud can improve end-user performance and experience. Cloud-hosted applications and websites can be easily scaled to serve more users or with higher throughput, and can run in geographic locations close to end users to reduce network latency.
Digital experience : users can access cloud services and data from anywhere, whether they are employees or customers. Contributes to the digital transformation, provides a better customer experience and provides employees with modern, flexible tools
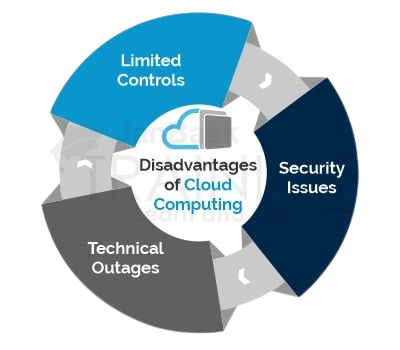
What are the Common Cloud Migration Disadvantages?
Cloud migration can be complicated and risky. Here are some of the major issues many organizations face when migrating resources to the cloud:
1- Lack of strategy : Many organizations are beginning to migrate to the cloud without devoting enough time and attention to their strategy. Successful adoption and implementation of the cloud requires strict comprehensive cloud migration planning. Each application and dataset may have different requirements and considerations and may require a different approach to cloud migration. Organizations must have a clear business case for each workload they migrate to the cloud
2-Cost management: When migrating to the cloud, many organizations do not have clear KPIs to understand what they plan to spend or save after migration. This makes it difficult to understand whether migration is economically successful. In addition, cloud environments are dynamic and can increase in costs quickly as new services are adopted and application usage increases.
3-Vendor Lock-In : Cloud providers offer many different services but many of them cannot be extended to other cloud platforms. Moving tasks from one cloud to another is a long and expensive process. Many organizations start using cloud services and later find it difficult to migrate providers if the current provider does not meet their requirements.
4-Data & Security Compliance : Cloud services use a shared responsibility model where they are responsible for securing the infrastructure and the customer is responsible for securing data and workloads. Therefore, while a cloud provider can provide robust security measures, it is the responsibility of your organization to properly configure them and ensure that all services and applications have adequate security controls. The migration process itself poses security risks. Transferring large amounts of data that can be sensitive and configuring access control for applications in different environments pose a significant risk.
What is migration in information Technology?
Domain servers’ consolidation and migration is a collection of documentation that presents a prescriptive, tested and supported approach to planning, designing, deploying, and verifying a domain migration project. The term “migration” in information technology refers to the process of converting data processing or information systems to a new technology. The terms “porting” and “migration” are frequently used interchangeably. Because migration can influence a variety of components in an information technology system, the term migration can be used to refer to both the conversion as a whole and specific components. Software, data, hardware, and apps are examples of components that may be affected. Individual phases must often be processed before the conversion, which includes all affected components, may be finished.
What are different migration strategies?
Depending on the type of migration to be undertaken, different strategies are employed. The ‘Chicken Little’ technique involves multiple tiny, incremental individual stages that are completed sequentially to keep migration manageable. The ‘Big Bang’ technique, on the other hand, accomplishes the actual conversion in a single, final step. The new system is first installed and tested alongside the old one. If the new system performs as expected, the old system is turned off and the new system is activated.
What are migration requirements?
To be considered successful, a migration must meet a number of criterias. It is critical to guarantee that the service is not stopped, or is interrupted as little as possible during the conversion. To reduce the danger of service interruptions, the number of changes should be kept to a minimum. However, the adjustments must be substantial enough to ensure that the new system meets all of the standards. Both contradictory requirements are satisfied by a successful migration.