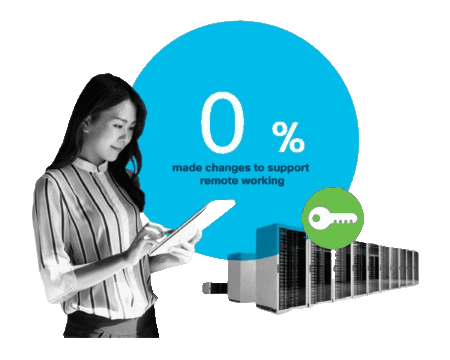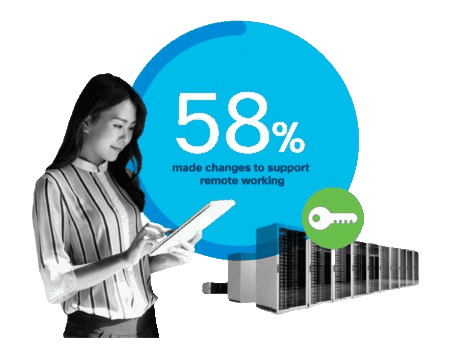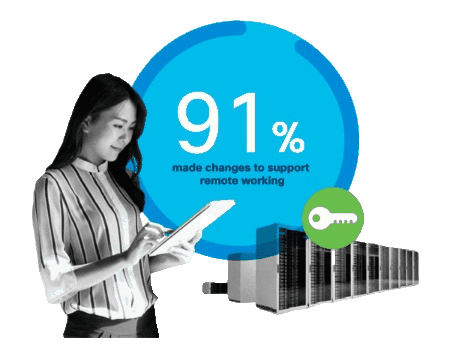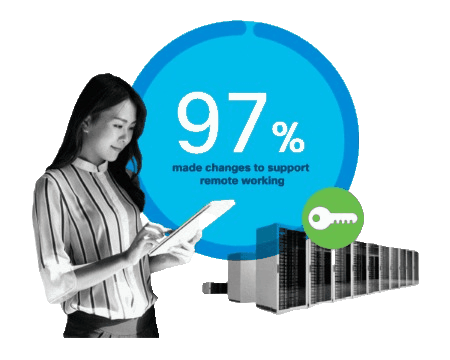
What is Remote Access?
- Remote access is the ability for an authorized user to connect to a computer or network from a different location using a network connection.
- Users can connect to the systems, computers or servers they require through remote access even if they are physically far away. This is crucial for workers who telecommute, travel, or work out of branch offices.
- Users who are located remotely can at any time access data and other system resources from any servers or devices that are linked to the network. Employee productivity rises as a result, and employees are better able to work with colleagues throughout the world.
- Technical support staff members at SoftFlow’s can connect remotely to users’ computers to assist them in resolving problems with their software or systems.
How do you obtain remote access?
- A virtual private network (VPN) connection for remote access is a popular way to grant remote access. An encrypted and secure connection is established via a VPN over a less secure network, such the internet.
- For branch offices and distant users to securely access business applications and other resources, VPN technology was created. Organizations can also employ multifactor authentication to confirm a user’s identification by combining various credentials that are specific to one individual.
How do businesses use remote access?
- Remote desktops are a tool that businesses can employ to give people remote access to their networks and applications. Application software, which is sometimes built into the operating system (OS) of the remote host, is used by remote desktops to allow programs to operate remotely on a network server and be shown locally at the same time.
- With a number of authentication techniques, including remote single sign-on, users may easily and securely access on-premises and cloud applications and servers from anywhere, on any device, without installing VPNs or changing firewall restrictions.
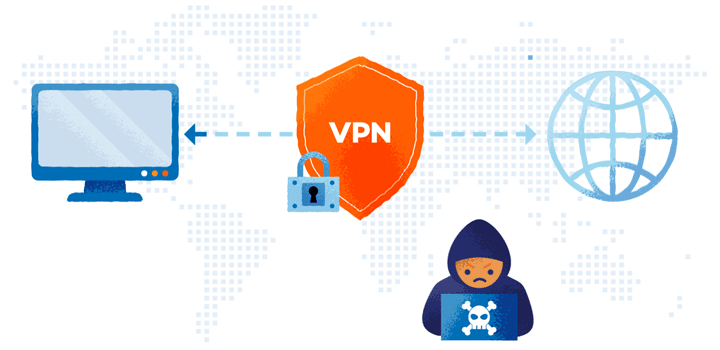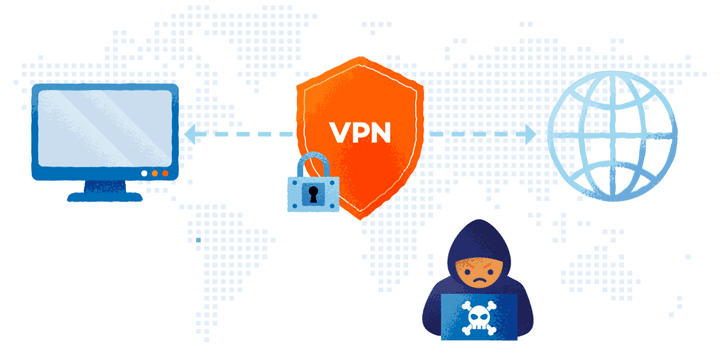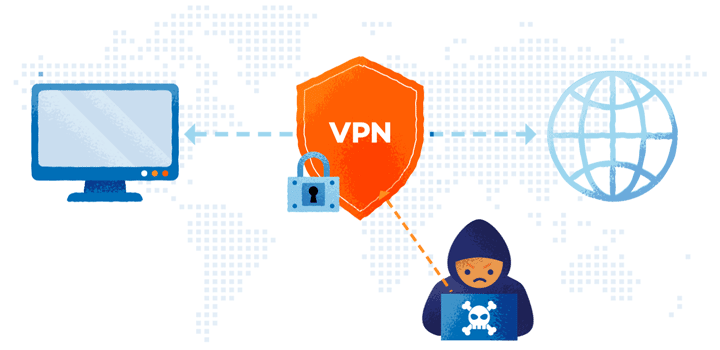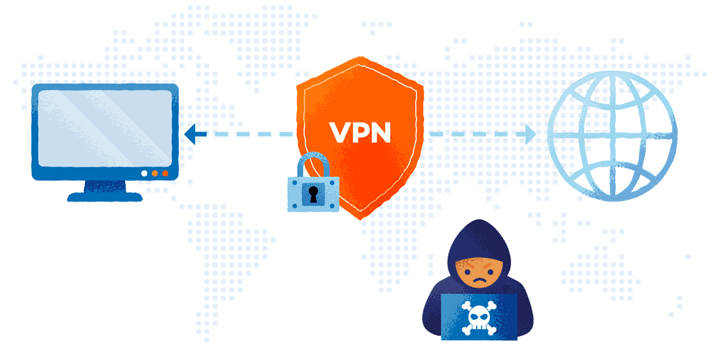
What is a VPN?
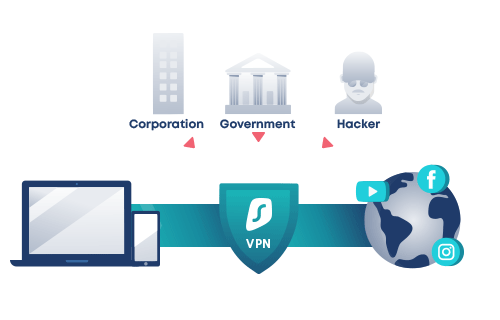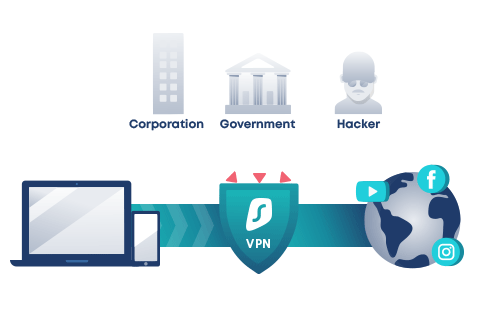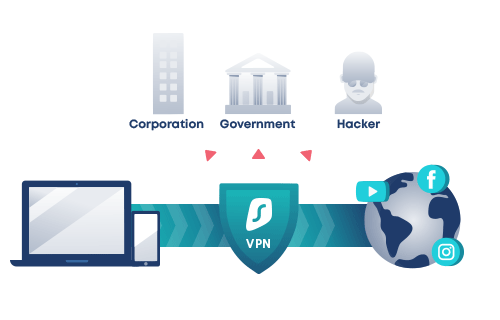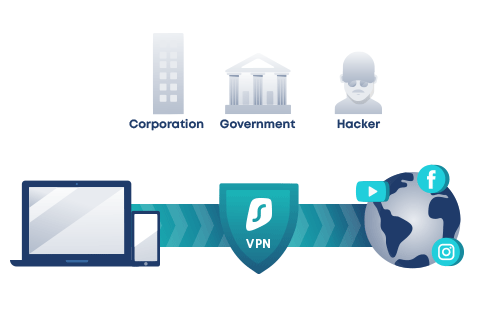
- Virtual private network, or VPN, is a service that safeguards your internet connection and online privacy.
- You may use public Wi-Fi hotspots with confidence since a VPN creates an encrypted tunnel for your data, hides your IP address to safeguard your online identity, and encrypts the data itself.
Why is a VPN necessary?
Everyone dislikes being observed or followed, especially if they have nothing to conceal. You must therefore improve your privacy practices. Your traffic is encrypted when you browse over a VPN, making it impossible for anyone to see what you do online. You require a VPN for the following reasons, among others:
What is a remote access VPN?
By encrypting all of the traffic that users send and receive, a remote access virtual private network (VPN) enables users who are working remotely to safely access and use apps and data that are housed in the corporate data center and headquarters.
What does a VPN do?
VPN changes your IP and masks your virtual location:
People working in countries with limited freedom of speech rely on private internet connection for their work. Sometimes, their lives might depend on it. Someone who lives under an authoritarian regime should use a VPN to hide their IP address and ensure extra security for their sensitive messages.
Data encryption using a VPN:
Even while browsing from your personal computer, using a VPN is a good idea. When you wish to secure your internet traffic and reduce your digital footprint, VPN encryption is crucial. By doing this, your internet service provider will be unable to sell the highest bidder your whole browsing history.
Protect your devices:
Your device will be protected from common internet threats including malware in downloaded files, web trackers, flashy advertisements, and harmful links thanks to VPN’s threat protection functions.
In what ways do VPN servers work?
- Your device transmits encrypted data to the VPN server when the VPN tunnel has been formed, including the website you want to browse. It decrypts it before sending the data to the specified web server. In addition, before transferring the data, it conceals your true IP address. Instead, the IP address of the VPN server you’re connecting to will appear to be yours.
- The VPN server encrypts the data and transmits it to you via your ISP when the web server answers. The data will be decrypted once it gets to your device by your VPN client.